Union Budget of India - Comparative Analysis
India is presently on its way to becoming an open market economy. It was during the 1990s that the national administration decided to start the process of economic liberalization by taking steps such as industrial deregulation, reducing controls on foreign investment and trade, and privatizing state held organizations.
In 2010 when the global economic meltdown was at a critical stage, India was among the stronger performers with a growth rate of more than 8 percent in real terms. This was fueled primarily by strong domestic demand.
Though India's economic growth has slowed down owing to factors such as high interest and inflation rates and lack of successful economic reforms. The global prices of crude oil have increased. Indian economy has also been affected by corruption in 2011 as continued problems have hampered effective implementation of reforms. However, the country still has a positive economic outlook for the medium term because of a young population that has low dependency ratio.
As per the International Monetary Fund, India is the 10th biggest economy in 2011 in terms of market exchange rates and third biggest with regards to purchasing power parity.
However, these efforts have helped a lot in the growth of Indian Economy.
Last Updated on 2/10/2012
In 2010 when the global economic meltdown was at a critical stage, India was among the stronger performers with a growth rate of more than 8 percent in real terms. This was fueled primarily by strong domestic demand.
Though India's economic growth has slowed down owing to factors such as high interest and inflation rates and lack of successful economic reforms. The global prices of crude oil have increased. Indian economy has also been affected by corruption in 2011 as continued problems have hampered effective implementation of reforms. However, the country still has a positive economic outlook for the medium term because of a young population that has low dependency ratio.
Budgetary Reforms in India
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act 2003 was the latest effort of the Indian government and some state governments to start laws related to fiscal responsibility. This act was supposed to do away with revenue deficit and restrict the fiscal shortfall to specified limits. In the last few years the Union and the state governments have made various efforts to bring down their budget deficit by appointing bodies such as Expenditure Commissions.India Budget – Past Performance
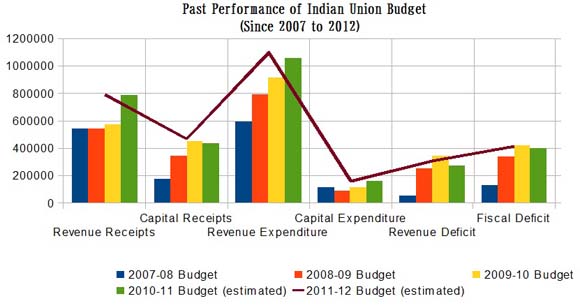
Following is a graphical representation of the same:
India Budget 2007-08
One of the major aspects of the 2007-08 union budget was targeting the high risk groups as part of the government's HIV/AIDS initiatives. The government also aimed to add 50 lakh farmers to the banking system in that period and set aside INR 500 crores for the National Agricultural Insurance Scheme. 100 crore rupees were also allocated for agricultural insurance in this fiscal.India Budget 2008-09
As per the 11th Five Year Plan INR 179,954 crores were allocated as part of the Central Plan and this was 16% higher than the previous fiscal. The Bharat Nirman project was supposed to be allotted 31,280 crore rupees. 130 crore rupees were allocated as part of the Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya program and 1000 scholarships were awarded as part of the National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship plan.India Budget 2009-10
In 2009-10 the union government increased its allocation to the National Highways Authority of India for the National Highway Development Programme by 23%. The Railways were provided 15,800 crore rupees. In the same period the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission received 12,887 crore rupees, which was 87% more than the previous fiscal. The allotment for providing basic facilities and housing to the urban poor in India was increased to INR 3,973 crores as well.India Budget 2010-11
As part of the 2010-11 budget the government increased its limit for Section 80C investments by 20 thousand rupees. It also waived off the excise duty on solar panels and exempted accredited news agencies from service taxes. The government also made account auditing regulatory for all earnings in excess of 15 lakh rupees. The tax net was also widened to include more services.India Budget 2011-12
One of the main aims of the 2011-12 budget was to make sure that the management system was more result oriented and transparent. It is expected that the budget will help India achieve a growth rate of 9%. The government has also targeted a revenue of 40,000 crore rupees from disinvestment. Public sector banks will be provided INR 6000 crore in that period so that they could have a minimum Tier I CRAR of 8%.However, these efforts have helped a lot in the growth of Indian Economy.
Last Updated on 2/10/2012
- Comparitive Analysis
- Union Budget Expectations
2013-14 - Union Budget 2011-12
- India Budget 2010-2011
- Union Budget 2010 Tax Proposals
- India Budget 2009
- Economy Survey
- Budget Speech
- Key to Budget
- Medium Term Fiscal Policy
- India National Budget
- Budget Announcements
- Budget Receipt
- Online Trading
- Infrastructure
- Memorandum
- Statement of Revenue Foregone
- Fiscal Policy Strategy
- India Budget 2010 Highlights
- Highlight of Union Budget 2011-2012
- 2012 Expectation
- 2011 Expectation
- Railway budget 2011-2012
- Railway budget 2010 2011
- 2010 Expectation
- Budget Highlights 2009
- India Budget 2008
- India's Union Budget 2008-09
- Increase in Tax Exemption limit
- Tax Benefits in Budget 2008
- Housing Sector In Budget 2008
- Income Tax Surcharge
- Service Tax in Budget 2008
- Infrastructure in Budget 2008
- Textile Sector in Budget 2008
- Direct Tax in Budget 2008
- Railway Budget 2008
- Macro Economic Framework



